

Aubrey de Grey. Aubrey David Nicholas Jasper de Grey (/dəˈɡreɪ/; born 20 April 1963[5])[6] is an English author and theoretician in the field of gerontology and the Chief Science Officer of the SENS Research Foundation.
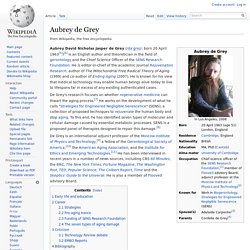
He is editor-in-chief of the academic journal Rejuvenation Research, author of The Mitochondrial Free Radical Theory of Aging (1999) and co-author of Ending Aging (2007). He is known for his view that medical technology may enable human beings alive today to live to lifespans far in excess of any existing authenticated cases. Early life and education[edit] De Grey was born and brought up in London, England.[12] He told The Observer that he never knew his father, and that his mother, an artist, encouraged him in the areas she herself was the weakest: science and mathematics.[3] He was educated at Sussex House School[13] and Harrow School. He attended the University of Cambridge, and studied at its constituent college of Trinity Hall.
Career[edit] Strategies[edit] Pro-aging trance[edit] Polony Multiplex Analysis of Gene Expression (PMAGE) in Mouse Hy. User:Ilya. Net Heads: Science News Online, Feb. 17, 2007. Genome@home. Today.reuters.com/news/articlenews.aspx. Giant Insects Might Reign If Only There Wa. The delicate lady bug in your garden could be frighteningly large if only there was a greater concentration of oxygen in the air, a new study concludes.
The study adds support to the theory that some insects were much larger during the late Paleozoic period because they had a much richer oxygen supply, said the study’s lead author Alexander Kaiser. The study, “No giants today: tracheal oxygen supply to the legs limits beetle size,’’ was presented at Comparative Physiology 2006: Integrating Diversity. The Paleozoic period, about 300 million years ago, was a time of huge and abundant plant life and rather large insects -- dragonflies had two-and-a-half-foot wing spans, for example.
The air’s oxygen content was 35% during this period, compared to the 21% we breathe now, Kaiser said. Researchers have speculated that the higher oxygen concentration allowed insects to grow much bigger. Tubes carry oxygen. Earths Hidden Biospheres. Biology News Net : Microarray Archive. The human genome complete sequencing project in 2003 revealed the enormous instruction manual necessary to define a human being.

However, there are still many unanswered questions. There are few indications on where the functional elements are found in this manual. To explain how we develop, scientists will have to decode the entire network of biological complexes that regulate development. One of the biggest challenges is to analyse the key proteins involved in the development of a human being, namely the proteins that bind to DNA. "If the genome provides the recipe to define a human being, the DNA proteins are the "chefs" that cook it", describes Herbert Auer, manager of the Functional Genomics Facility at the Institute for Research in Biomedicine (IRB Barcelona) and co-organizer, together with Erich Grotewold, at the Ohio State University, of the Barcelona Biomed Conference, "The DNA proteome".
Gene Expression. Ensembl Genome Browser. Manolis Kellis (Kamvysselis) Manolis Kellis, Ph.D.

Associate Professor with tenure MIT Computer Science and Electrical Engineering Department MIT Computational Biology Group, headComputer Science and Artificial Intelligence LaboratoryBroad Institute of MIT and HarvardStata Center - 32D.524 - 617.253.2419 (contact) Awards: - Presidential Early Career Award (PECASE) - Alfred P. Sloan Foundation Award - National Science Foundation CAREER Award - AIT Niki Award for Science and Engineering - Technology Review TR35 Top Young Innovators - Ruth and Joel Spira Teaching Award - MIT Sprowls Award for Best PhD Thesis in Computer Science. Luis Rochas Current Research Project. Complex Adaptive Systems and Computational Intelligence Almost all interesting processes in nature are highly cross linked.

In many systems, however, we can distinguish a set of fundamental building blocks, which interact nonlinearly to form compound structures or functions with an identity that requires more explanatory devices than those used to explain the building blocks. BioHacking. For those who are not aware of digital evolution, I am writing a quick short summary.

Digital evolution means evolution of computer programs who compete for limited resources such as CPU and memory. In short, it goes something like this: - You define a universe, which is virtual memory (space) and CPU (time) - You create energy (CPU cycles) - You define an extremely limited instruction set for Virtual Machine (Physics). Instruction set being limited is important because you want to mimic physics, not chemistry or biology - You seed randomly generated programs of varying length - You start parallel execution the random programs - Each instruction eats up energy and at random times you feed energy into universe - At random times mis-execute program instructions - Run it for a long time and Voila! Finally self replication gets evolved from very simple instructions - Then arms race gets started between programs and things get interesting. The Inner Life Of A Cell (HQ) The Inner Life Of A Cell - Hemmy.net, A so. The inner life of the cell.
CONSTRUCTIVE BIOLOGY. As creative as we become, and as industrious and as good as we are at designing and manufacturing living things, which we've been doing since the stone age — no matter how good we get at that, it's like calling a candle a supernova.

IT Conversations: Jerry Fiddler. In the not-too-distant future, the majority of electronic devices will be connected via the Internet or wireless protocols, bringing convenience and simplicity to daily living, but adding layers of technology and complexity to devices we use everyday.

Jerry Fiddler offers a glimpse to his vision of the future: "The Connected World. " He discusses how this "world system" will evolve through the convergence of multiple technologies resulting in one, giant interoperable system. The Nature Institute. This article first appeared in the January 25, 2005 issue of NetFuture.

In January, 1956, Herbert Simon, who would later win the Nobel prize in economics, walked into his classroom at Carnegie Institute of Technology and announced, "Over Christmas Allen Newell and I invented a thinking machine". Reaction-Diffusion. My thesis work was about creating synthetic texture using reaction-diffusion.
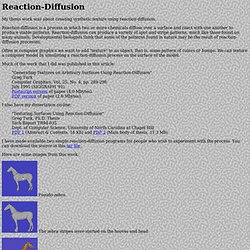
Reaction-diffusion is a process in which two or more chemicals diffuse over a surface and react with one another to produce stable patterns. Reaction-diffusion can produce a variety of spot and stripe patterns, much like those found on many animals. Developmental biologists think that some of the patterns found in nature may be the result of reaction-diffusion processes. Often in computer graphics we want to add "texture" to an object, that is, some pattern of colors or bumps. We can texture a computer model by simulating a reaction-diffusion process on the surface of the model. Biochemistry, tableofcontents. Alex Kosorukoff Publications. The MEL 1001 lab is now available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
An information page about the EWS performance improvement project is available. The Engineering WorkStation (EWS) labs currently include over 1,100 workstations and serve over 10,000 students taking Engineering courses. EWS provides high performance, highly reliable instructional computing environment for the students and faculty of the College of Engineering. For assistance with any EWS resource, please contact an on duty lab consultant, e-mail ews@illinois.edu or call EWS 9-5 M-F at 217-265-8161. Protein synthesis: an epic on the cellular level. Technology Review: TR35 - Manolis Kellis. Welcome to the Wong Lab.