

AreaNetworking.it - ICT Professionals Network. A proposito dell'autore Premessa Una VPN o Virtual Private Network è un modo economico e sicuro per consentire l’accesso ad una LAN da qualsiasi parte del mondo.
Le possibilità per la sua realizzazione sono molteplici: si va dalla soluzione hardware alla soluzione mista o solo software. Per ognuna di queste esistono a sua volta molte soluzioni che non staro’ pero’ qui ad elencare. Nel nostro caso siamo interessati soltanto al caso di VPN software e più in particolare alle soluzioni freeware o meglio ancora OpenSource. Introduzione alle VPN Innanzi tutto iniziamo dicendo cos’è una VPN e quali problematiche questa risolve. Vediamo quindi cosa è una VPN e come è possibile realizzarne una. FASE I: Ricerca delle soluzioni Facendo una breve ricerca su google ho individuato tre soluzioni che sono basate sui seguenti protocolli: IPSec, PPTP e SSL/TSL. PPTP è uno standard documentato e rilasciato dalla IETF nell’RFC 2637.
IPSec Vediamo un po’ il suo funzionamento. Dettagli Tecnici Configurazione . . . . How to configure a host as a gateway for client-side subnets. Site-to-Site Layer 2 Bridging Using OpenVPN Access Server and a Linux Gateway Client. Last modified: 18 April 2013 Introduction OpenVPN Access Server can be configured in a site-to-site bridging setup that allows you to transparently bridge two sites together using a OpenVPN gateway client.
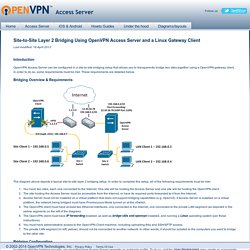
In order to do so, some requirements must be met. These requirements are detailed below. Bridging Overview & Requirements The diagram above depicts a typical site-to-site layer 2 bridging setup. You have two sites, each one connected to the Internet. Bridging Configuration In order to start the bridging process, you must first have Access Server generate an autologin profile. Now, login to the Client Web Server (CWS) and select the Login dropdown, when prompted. Download the autologin profile that is offered to you in the CWS. Download the following bridging scripts onto your computer:bridge-up.shbridge-down.sh Using a SFTP client such as Filezilla or Cyberduck, upload the ovpn profile, and the two bridging scripts you have downloaded, onto the Linux OpenVPN client machine.
Using DD-WRT with OpenVPN Access Server. Introduction Many of our users have expressed interest in using DD-WRT or related routers to connect to VPN servers hosted behind Access Server.
While using OpenVPN in this manner may not yield the best performance, due to the limited processing power and memory of the router, it could be useful in the cases where convenience, rather than high throughput, is required.Please note that the information provided here is for EDUCATION and INFORMATIONAL uses only. We are not responsible for any damages you incur as a result of using these instructions here. For technical support relating to the DD-WRT firmware, please visit the DD-WRT community forums. In order to configure DD-WRT for use in OpenVPN Access Server environments, you will first need to create and download the autologin profile from your server. Creating and Downloading the Autologin Profile Now, login to the Client Web Server (CWS) and select the Login dropdown, when prompted. Afterwards, visit the Services tab, then the VPN tab. HOWTO. Introduction OpenVPN is a full-featured SSL VPN which implements OSI layer 2 or 3 secure network extension using the industry standard SSL/TLS protocol, supports flexible client authentication methods based on certificates, smart cards, and/or username/password credentials, and allows user or group-specific access control policies using firewall rules applied to the VPN virtual interface.
OpenVPN is not a web application proxy and does not operate through a web browser. OpenVPN 2.0 expands on the capabilities of OpenVPN 1.x by offering a scalable client/server mode, allowing multiple clients to connect to a single OpenVPN server process over a single TCP or UDP port. OpenVPN 2.3 includes a large number of improvements, including full IPv6 support and PolarSSL support. This document provides step-by-step instructions for configuring an OpenVPN 2.x client/server VPN, including: The impatient may wish to jump straight to the sample configuration files:
Setting your client to automatically connect to your VPN when your computer starts. In order to automatically connect to your VPN when your computer starts you will need to login to the Connect Client as a user who has an autologin profile allocated to them.
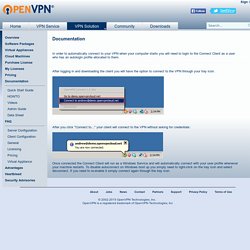
After logging in and downloading the client you will have the option to connect to the VPN through your tray icon: After you click "Connect to... " your client will connect to the VPN without asking for credentials: Once connected the Connect Client will run as a Windows Service and will automatically connect with your user profile whenever your machine restarts. To disable autoconnect on Windows boot up you simply need to right-click on the tray icon and select disconnect. How do I setup OpenVPN Access Server to use site-to-site? If you want to have two access servers connected to each other via site-to-site you will need to have gateway functionality enabled somewhere on the network of one of your Access Servers. · I will refer to the two access servers we want to connect as AS1 (Access Server 1) and AS2 (Access Server 2). · Now in order to get a tunnel established between AS1 and AS2 we will need to setup a gateway client on one of the LAN'S for either AS1 or AS2. · By setting up the gateway client it will connect to a remote access server (AS1) and push the routes from the access server(AS1) to the LAN(AS2) and push its LAN's(AS2) routes to the remote Access Server(AS1).
