

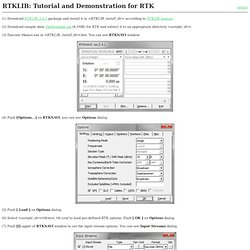
An Open Source Program Package for GNSS Positioning. (1) Download RTKLIB_2.4.1 package and install it to <RTKLIB_install_dir> according to RTKLIB manual.
RTKLIB on the Raspberry Pi. I've got a workmate.
He wants to build an autonomous, electric, rotary hoe. Anyway, he needs to locate the hoe to within a few centimetres. I'd been contemplating DGPS for a while as I've found GPS tracks are a bit wandery when logging tracks for OpenStreetMap. I thought it'd be a good capability to have, so I've stepped up to the task of tracking Robohoe. Background Information This is basically a link dump of what I've found so far: RTKLIB : DGPS software This is the bees knees for cheap arse DGPS. It's also got a number of other super handy programs, that do things like convert RTKLIB output into a Google Earth KML file, serve serial input out to multiple processes via Unix sockets etc. (1) Cost-effective precise positioning using carrier phase navigation-grade receiver.
Fig. 3.
Cost-effective baseline ellipses and their orientation covariance matrix, and provide a graphical means of viewingthe post-processing results.In order to evaluate the accuracy of the cost-effective base-line vector solutions, the same baselines were also measuredwith professional, geodetic-grade equipment. The collecteddual-frequency data along with the Topcon Tools softwarewere used to estimate the geodetic baseline vectors. TableII displays the low-cost baseline errors with respect to thegeodetic baselines along each baseline component. The resultsindicate an agreement on centimeter level, with errors below. LEA-6_DataSheet_(GPS.G6-HW-09004).pdf.
Gpspp.sakura.ne.jp/paper2005/isgps2008_paper_ttaka.pdf. Isgps_2009_rtklib_revA.pdf. Odot_ref_net.pdf. Manual_2.4.2.pdf. Open Source GPS-related discussion and support. Isgps2008_paper_ttaka.pdf.
Www.u-blox.com/images/downloads/Product_Docs/LEA-4T_Prod_Summary(GPS.G4-MS4-05069-B).pdf. Docs.swift-nav.com/pdfs/piksi_datasheet_v2.3.1.pdf. Precision GNSS + Inertial - GNSS Positioning. RTK Systems - Navipedia. From Navipedia With origin dating back to the mid-1990s, Real Time Kinematics (RTK) is a differential GNSS technique which provides high positioning performance in the vicinity of a base station.
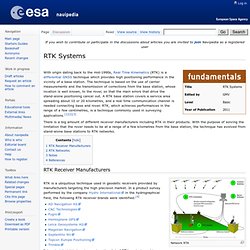
The technique is based on the use of carrier measurements and the transmission of corrections from the base station, whose location is well known, to the rover, so that the main errors that drive the stand-alone positioning cancel out. A RTK base station covers a service area spreading about 10 or 20 kilometres, and a real time communication channel is needed connecting base and rover. RTK, which achieves performances in the range of a few centimetres, is a technique commonly used in surveying applications.[1][2][3] There is a big amount of different receiver manufacturers including RTK in their products. RTK Receiver Manufacturers. Carrier Phase Ambiguity Fixing - Navipedia. From Navipedia The carrier phase measurements are much more precise than the code pseudorange measurements (typically, about two orders of magnitude), but they contain the unknown ambiguities (B), (see Linear observation model for PPP).
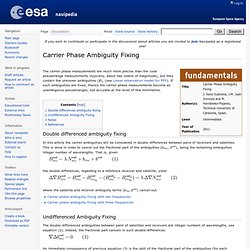
If such ambiguities are fixed, thence the carrier phase measurements become as unambiguous pseudoranges, but accurate at the level of few millimetres. Double differenced ambiguity fixing In this article the carrier ambiguities will be considered in double differences between pairs of receivers and satellites. This is done in order to cancel out the fractional part of the ambiguities (brec, bsat), being the remaining ambiguities integer number of wavelengths. The double differences, regarding to a reference receiver and satellite, yield: where the satellite and receiver ambiguity terms (brec,bsat) cancel-out.
Carrier phase ambiguity fixing with two frequencies Carrier phase ambiguity fixing with three frequencies Undifferenced Ambiguity Fixing Notes References. Real Time Kinematics - Navipedia. From Navipedia With origin dating back to the mid-1990s, Real Time Kinematics (RTK) is a differential GNSS technique which provides high positioning performance in the vicinity of a base station.
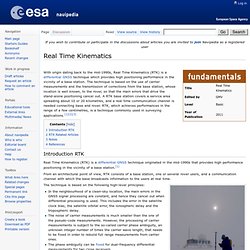
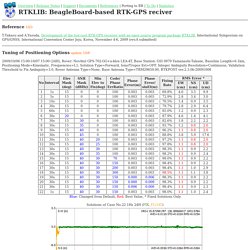
The technique is based on the use of carrier measurements and the transmission of corrections from the base station, whose location is well known, to the rover, so that the main errors that drive the stand-alone positioning cancel out. A RTK base station covers a service area spreading about 10 or 20 kilometres, and a real time communication channel is needed connecting base and rover. RTK, which achieves performances in the range of a few centimetres, is a technique commonly used in surveying applications.[1][2][3] Introduction RTK Real Time Kinematics (RTK) is a differential GNSS technique originated in the mid-1990s that provides high performance positioning in the vicinity of a base station.[1] RTK Support Polar Survey. LEA-4T_Prod_Summary(GPS.G4-MS4-05069-B).pdf. RTKLIB: Porting for Beagle Board. Reference 10/3 T.Takasu and A.Yasuda, Development of the low-cost RTK-GPS receiver with an open source program package RTKLIB, International Symposium on GPS/GNSS, International Convention Center Jeju, Korea, November 4-6, 2009 (rev.A submitted) Tuning of Positioning Options update 10/8 2009/10/06 15:00-10/07 15:00 (24H), Rover: NovAtel GPS-702-GG+u-blox LEA-4T, Base Station: GSI 0979 Yamanashi-Takane, Baseline Length=6.1km, Positioning Mode=Kinematic, Frequencies=L1, Solution Type=Forward, Iono/Tropos Est=OFF, Integer Ambiguity Resolution=Continuous, Validation Threshold to Fix Ambiguity=3.0, Rover Antenna Type=None, Base Antenna Type=TRM29659.00, RTKPOST ver.2.3.0b-20091008 Blue: Changed from Default, Red: Best Value, * Fixed Solutions Only Solutions of Case No.22 1Hz 24H (FIX, FLOAT)
Regular GPS not accurate enough? Try RTK-GPS! Centimeter-level precision GPS for $900. Real Time Kinematic. Overview[edit] Background[edit] Normally, satellite navigation receivers must align signals sent from the satellite to an internally generated version of a pseudorandom binary sequence, also contained in the signal.
Since the satellite signal takes time to reach the receiver, the two sequences do not initially coincide; the satellite's copy is delayed in relation to the local copy. By increasingly delaying the local copy, the two copies can eventually be aligned. The correct delay represents the time needed for the signal to reach the receiver, and from this the distance from the satellite can be calculated. RTKLIB: An Open Source Program Package for GNSS Positioning. Piksi User Getting Started Guide - Swift Navigation Wiki. This is a guide to getting started using the Swift Navigation Piksi GPS Receiver.
It will provide an overview of how to setup the device for the first time, connect to it and view position solutions and status information. This guide was tested on Linux (Ubuntu 12.10 32-bit, kernel version 3.5.0-17), OS X (10.8.5), and Windows XP (SP3) installations. If you want to set up the toolchain to build firmware for Piksi, see the Piksi Developer Getting Started Guide. If anything in this guide is incorrect or unclear, please email our mailing list.