

Probability. These concepts have been given an axiomatic mathematical formalization in probability theory (see probability axioms), which is used widely in such areas of study as mathematics, statistics, finance, gambling, science (in particular physics), artificial intelligence/machine learning, computer science, and philosophy to, for example, draw inferences about the expected frequency of events.
Probability theory is also used to describe the underlying mechanics and regularities of complex systems.[4] Interpretations[edit] When dealing with experiments that are random and well-defined in a purely theoretical setting (like tossing a fair coin), probabilities can be numerically described by the statistical number of outcomes considered favorable divided by the total number of all outcomes (tossing a fair coin twice will yield head-head with probability 1/4, because the four outcomes head-head, head-tails, tails-head and tails-tails are equally likely to occur). Sets, Counting, and Probability. Oli.extension.harvard.edu. Symmetry in mathematics. In general, every kind of structure in mathematics will have its own kind of symmetry, many of which are listed in this article.
Symmetry in geometry[edit] The types of symmetry considered in basic geometry (like reflection and rotation symmetry) are described more fully in the main article on symmetry. Abstract symmetry[edit] Klein's view[edit] Thurston's view[edit] William Thurston introduced a similar version of symmetries in geometry. A model geometry is called maximal if G is maximal among groups acting smoothly and transitively on X with compact stabilizers, i.e. if it is the maximal group of symmetries. A geometric structure on a manifold M is a diffeomorphism from M to X/Γ for some model geometry X, where Γ is a discrete subgroup of G acting freely on X. A 3-dimensional model geometry X is relevant to the geometrization conjecture if it is maximal and if there is at least one compact manifold with a geometric structure modelled on X.
Symmetry in calculus[edit] Even functions[edit] or. Poker probability. In poker, the probability of each type of 5-card hand can be computed by calculating the proportion of hands of that type among all possible hands.
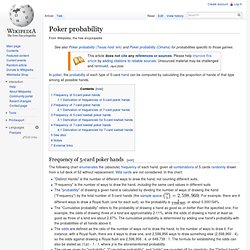
Frequency of 5-card poker hands[edit] "Distinct Hands" is the number of different ways to draw the hand, not counting different suits. "Frequency" is the number of ways to draw the hand, including the same card values in different suitsThe "probability" of drawing a given hand is calculated by dividing the number of ways of drawing the hand ("Frequency") by the total number of 5-card hands (the sample space; ). For example, there are 4 different ways to draw a Royal flush (one for each suit), so the probability is 4/2,598,960, or about 0.000154%.The "Cumulative probability" refers to the probability of drawing a hand as good as or better than the specified one.
For example, the odds of drawing three of a kind are approximately 2.11%, while the odds of drawing a hand at least as good as three of a kind are about 2.87%. As above. . . There are. American Roulette Probabilities. Here are a few useful probabilities for American roulette.
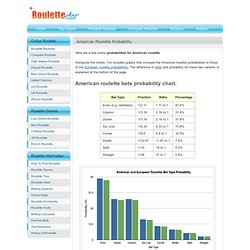
Alongside the charts, I've included graphs that compare the American roulette probabilities to those of the European roulette probabilities. The difference in odds and probability for these two variants is explained at the bottom of the page. American roulette bets probability chart. A simple bar chart to highlight the percentage probabilities of winning with the different bet types in American and European roulette. Same even money bet result in a row probability. When playing on an American roulette wheel, what's the probability of seeing the same colour appear X times in a row? Example: The probability of the same colour showing up 6 times in a row on an American roulette wheel is 1.13%. A graph to show the probability of seeing the same colour of red/black on an American roulette table (compared to the odds on a European table).
Random American roulette probabilities.